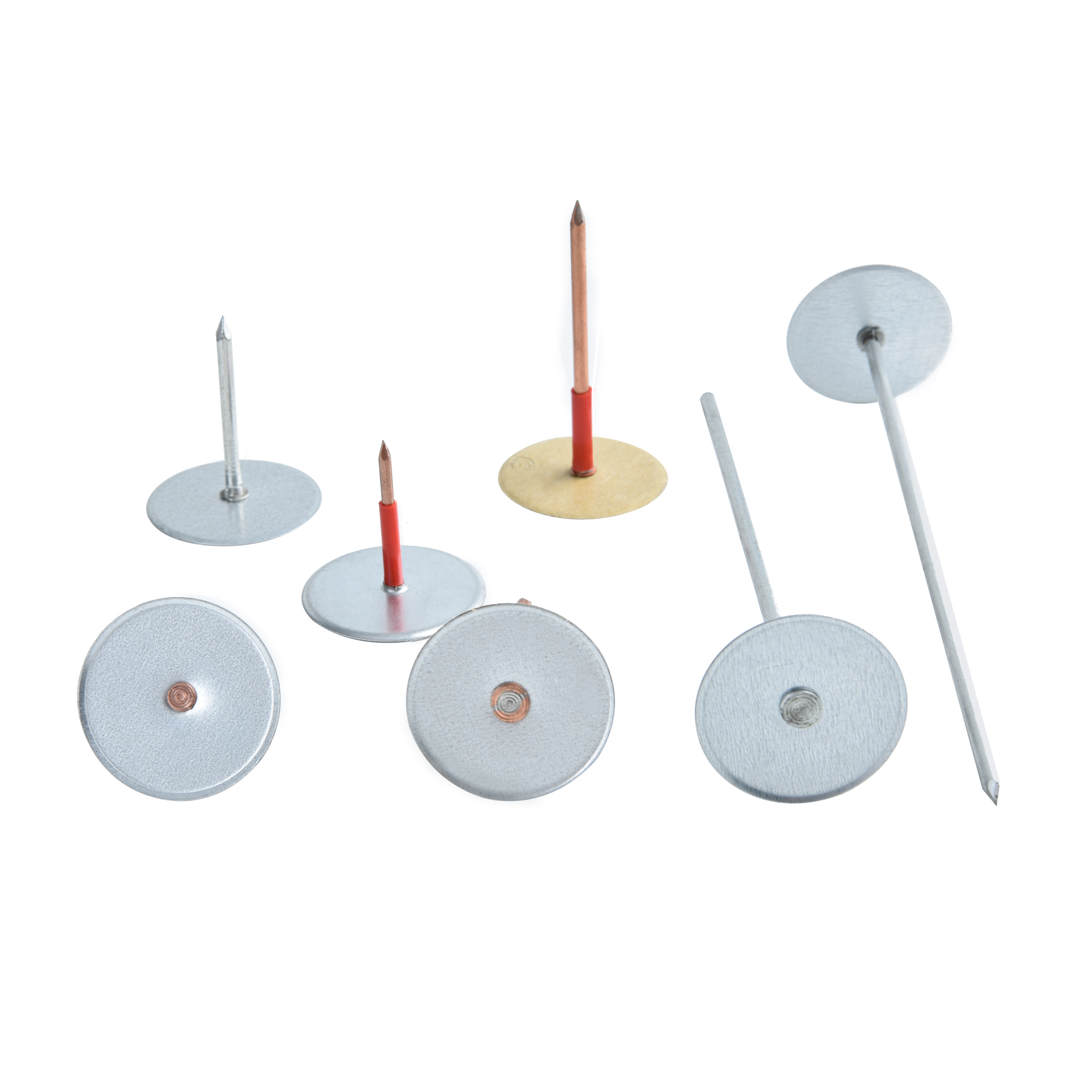
Mild steel cupped head weld pins
Mild steel cupped head weld pins are specialized fastening components that combine the characteristi
Contact
Product Detail
Mild steel cupped head weld pins are specialized fastening components that combine the characteristics of mild steel material, a cupped head design, and a welding - based attachment method. These pins play a crucial role in various industrial, construction, and manufacturing applications, offering a reliable and efficient way to join materials together. This article will explore each aspect of the term in detail, including the properties of mild steel, the functionality of the cupped head, the significance of the welding feature, and the wide - ranging applications of these pins.
Mild Steel: The Material Choice
Mild steel, also known as low - carbon steel, is the primary material used in these pins. It typically contains a carbon content ranging from 0.05% to 0.25%, which gives it several distinct properties that make it suitable for a variety of applications. One of the key advantages of mild steel is its excellent formability. Due to its relatively low carbon content, mild steel can be easily shaped through processes such as rolling, forging, and machining. This allows manufacturers to produce weld pins in the desired cupped head shape with precision, ensuring consistent quality and performance.
Another important property of mild steel is its good weldability. Welding is a critical process for attaching the weld pins to other materials, and mild steel readily forms strong, reliable welds. When heated during the welding process, mild steel melts and fuses with the base material, creating a permanent bond. This weldability makes mild steel cupped head weld pins an ideal choice for applications where a secure and durable connection is required. Additionally, mild steel offers a good balance between strength and ductility. It has sufficient strength to withstand normal mechanical loads in most applications, while its ductility allows it to deform slightly under stress without breaking, providing a certain degree of flexibility and shock absorption.
Cost - effectiveness is also a significant factor in the use of mild steel for these pins. Compared to high - strength or alloy steels, mild steel is relatively inexpensive, which helps to keep the production costs of the weld pins down. This makes mild steel cupped head weld pins a practical and economical fastening solution, especially for large - scale projects where a large number of pins are required. However, it's important to note that mild steel has lower corrosion resistance compared to some other materials, such as stainless steel. In applications where exposure to moisture, chemicals, or harsh environments is expected, additional protective measures, such as painting, galvanizing, or applying anti - corrosion coatings, may be necessary to prevent rust and extend the lifespan of the pins.
Cupped Head: Design Advantages
The “cupped head” design of these pins offers several functional and practical benefits. Similar to other cupped head fasteners, the cup - shaped head of mild steel cupped head weld pins provides a larger surface area for contact with the material being fastened. When welded in place, this increased surface area helps to distribute the load more evenly across the joint, reducing the risk of stress concentrations that could lead to cracking or failure of the weld or the base material. This is particularly important in applications where the pins are subjected to dynamic loads, vibrations, or heavy mechanical stresses, such as in the construction of bridges, buildings, and heavy machinery.
The cupped head design also enhances the visual appearance of the fastened assembly. In some applications where the pins are visible, such as in decorative metalwork or architectural installations, the rounded and smooth shape of the cupped head can add an aesthetically pleasing element to the overall design. Moreover, the cupped head can act as a protective cover for the weld joint. It helps to shield the weld from external impacts, abrasion, and environmental factors, which can contribute to the long - term durability and reliability of the connection.
From an installation perspective, the cupped head design makes it easier to position and align the pins during the welding process. The distinct shape of the cup provides a clear target for the welder, allowing for more accurate placement of the pin. This can improve the efficiency of the assembly process, especially in automated manufacturing lines where precise and consistent welding is required.
Weld Pins: The Attachment Method
The “weld” feature of these pins is what sets them apart from other types of fastening components. Welding mild steel cupped head pins offers several advantages over traditional mechanical fastening methods, such as screwing or bolting. Firstly, welding creates a permanent and seamless connection. Once the pin is welded to the base material, there are no moving parts or threads that can loosen over time due to vibrations or mechanical stress. This results in a more secure and reliable joint, which is essential in applications where the integrity of the connection is critical, such as in structural engineering and heavy - duty machinery.
Secondly, welding allows for greater design flexibility. Weld pins can be attached to a wide variety of materials, including other metals, alloys, and even some non - metallic materials with appropriate surface treatments. This versatility enables designers and engineers to create complex and customized assemblies that meet specific performance requirements. Additionally, welding can be used to join materials of different thicknesses and shapes, providing a solution for challenging fastening applications where traditional methods may not be suitable.
The welding process for mild steel cupped head weld pins typically involves several steps. First, the surfaces of the pin and the base material are cleaned to remove any dirt, grease, or oxidation that could interfere with the welding process. Then, the pin is positioned accurately on the base material, and a welding technique, such as arc welding, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, or TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, is used to melt the materials at the joint and form a bond. The choice of welding method depends on factors such as the thickness of the materials, the required welding speed, and the quality of the weld. After welding, the joint may be inspected for quality, and any necessary post - weld treatments, such as grinding or polishing, may be carried out to ensure a smooth and finished appearance.
Applications of Mild Steel Cupped Head Weld Pins
The unique combination of mild steel material, cupped head design, and welding functionality makes these pins suitable for a diverse range of applications.
In the construction industry, mild steel cupped head weld pins are used for structural connections. They can be used to join steel beams, columns, and other structural components, providing a strong and reliable fastening solution. In building facades, these pins can be used to attach metal panels, cladding, or decorative elements, ensuring both structural integrity and an aesthetically pleasing appearance.
In the automotive industry, weld pins are employed in the assembly of vehicle frames, chassis, and body panels. The ability to create strong and permanent welds is crucial for ensuring the safety and durability of automobiles. Mild steel cupped head weld pins can also be used in the manufacturing of automotive components, such as engine mounts, suspension parts, and exhaust systems, where a secure and vibration - resistant connection is required.
In the manufacturing of industrial machinery and equipment, these pins play a vital role in the assembly process. They can be used to fasten various components, such as gears, shafts, and housings, ensuring the proper functioning and reliability of the machinery. In the production of metal furniture, mild steel cupped head weld pins can be used to join metal frames and parts, providing a sturdy and long - lasting construction.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
The production of mild steel cupped head weld pins involves a series of processes to ensure consistent quality and performance. The mild steel raw material is first processed into the desired pin shape, which may include cutting, shaping, and forming operations. Then, the cupped head is created through processes such as cold heading or machining. After that, the pins may undergo heat treatment to improve their mechanical properties, such as strength and hardness.
Quality control is an essential part of the manufacturing process. Pins are inspected for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and mechanical properties. Weldability tests are also conducted to ensure that the pins can form strong and reliable welds. Additionally, non - destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing or X - ray inspection, may be used to detect any internal defects or flaws in the pins. Only pins that meet the strict quality standards are approved for use, ensuring the reliability and safety of the final products in which they are incorporated.
In conclusion, mild steel cupped head weld pins are versatile and reliable fastening components that offer a combination of material properties, design features, and attachment methods suitable for a wide range of applications. Their use in various industries contributes to the creation of strong, durable, and efficient structures and products. As manufacturing technologies and materials science continue to advance, these pins are likely to evolve and find even more applications in the future.